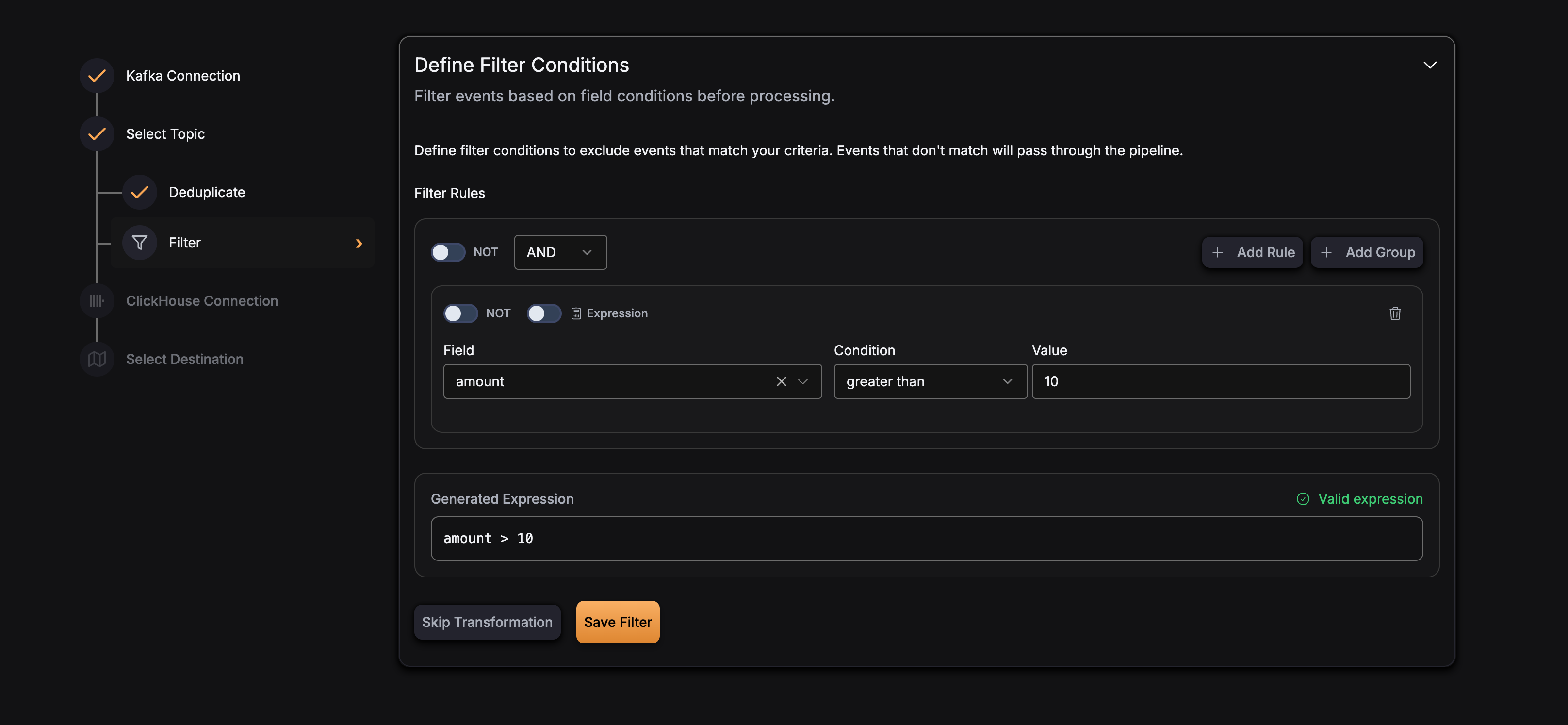
Filter
The Filter transformation allows you to selectively process events based on configurable expressions. Events that match the filter expression are processed further in the pipeline, while non-matching events are filtered out and not processed.
How It Works
Filtering in GlassFlow is applied at the ingestor stage, before any other processing. The filter uses expression-based evaluation to determine whether an event should be processed.
Internal Process
- Event Reception: Events are received from Kafka topics
- Expression Evaluation: Each event is evaluated against the configured filter expression
- Filtering Decision:
- If the expression evaluates to
true, the event is processed further - If the expression evaluates to
false, the event is filtered out
- If the expression evaluates to
- Processing: Only matching events continue through the pipeline (deduplication, join, sink)
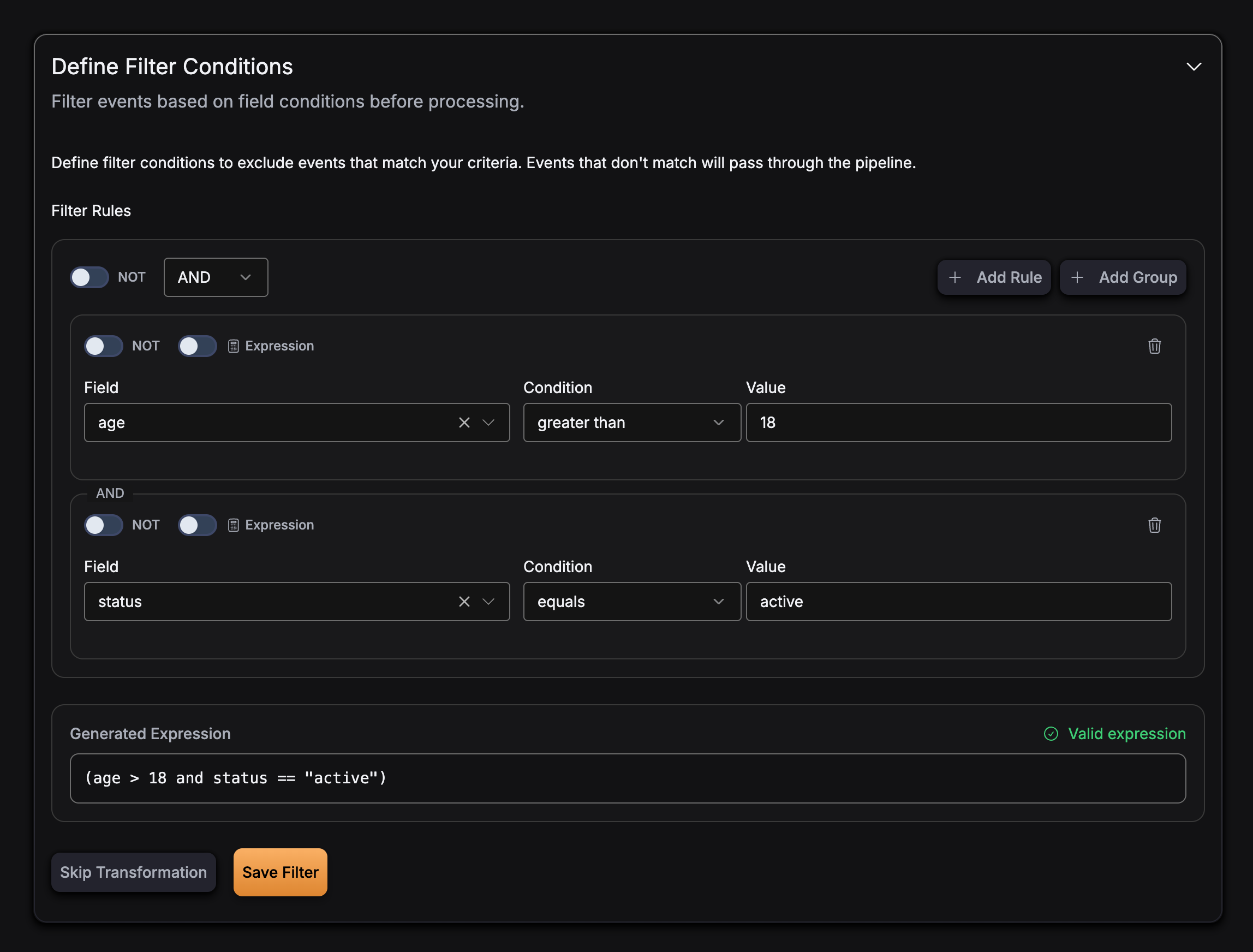
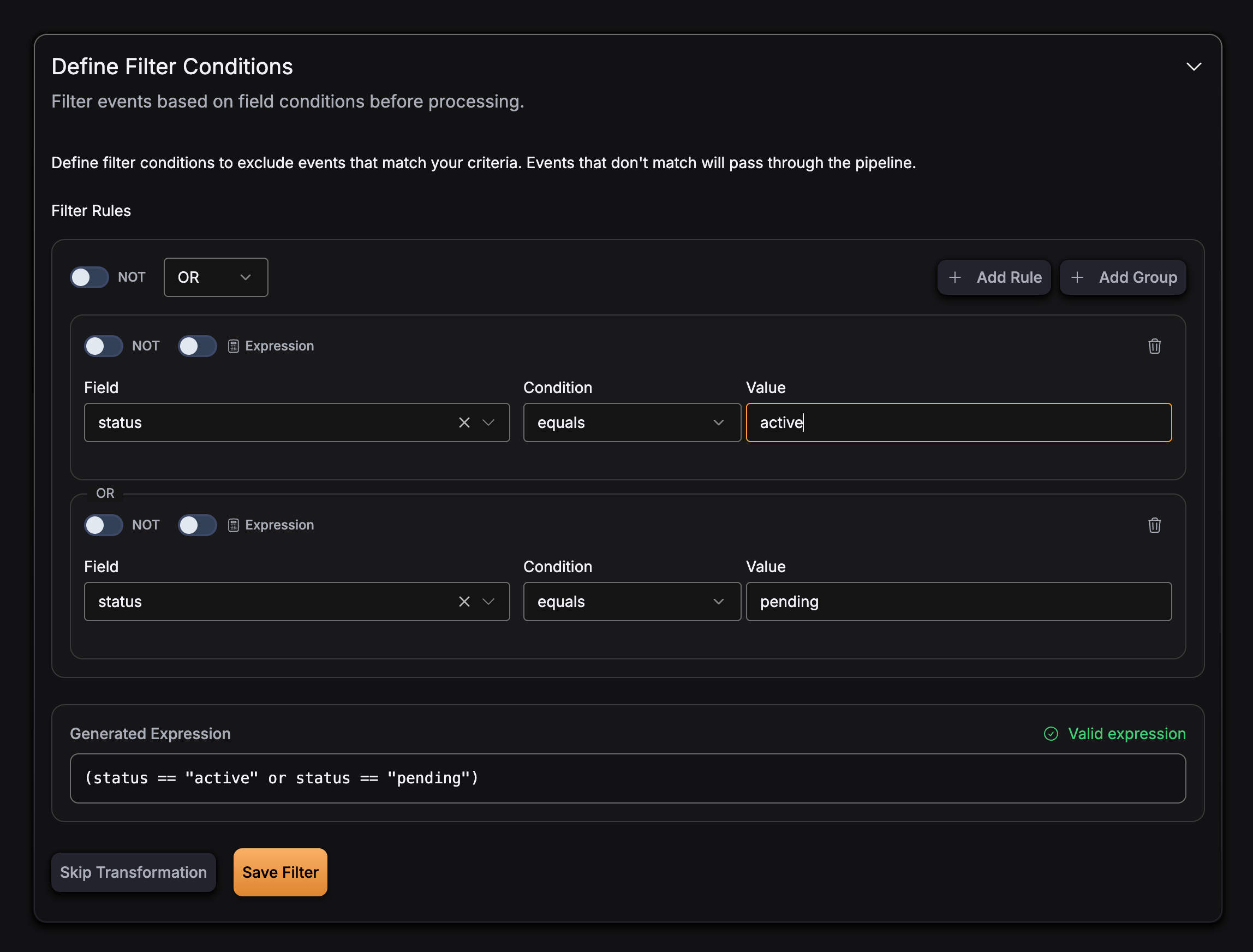
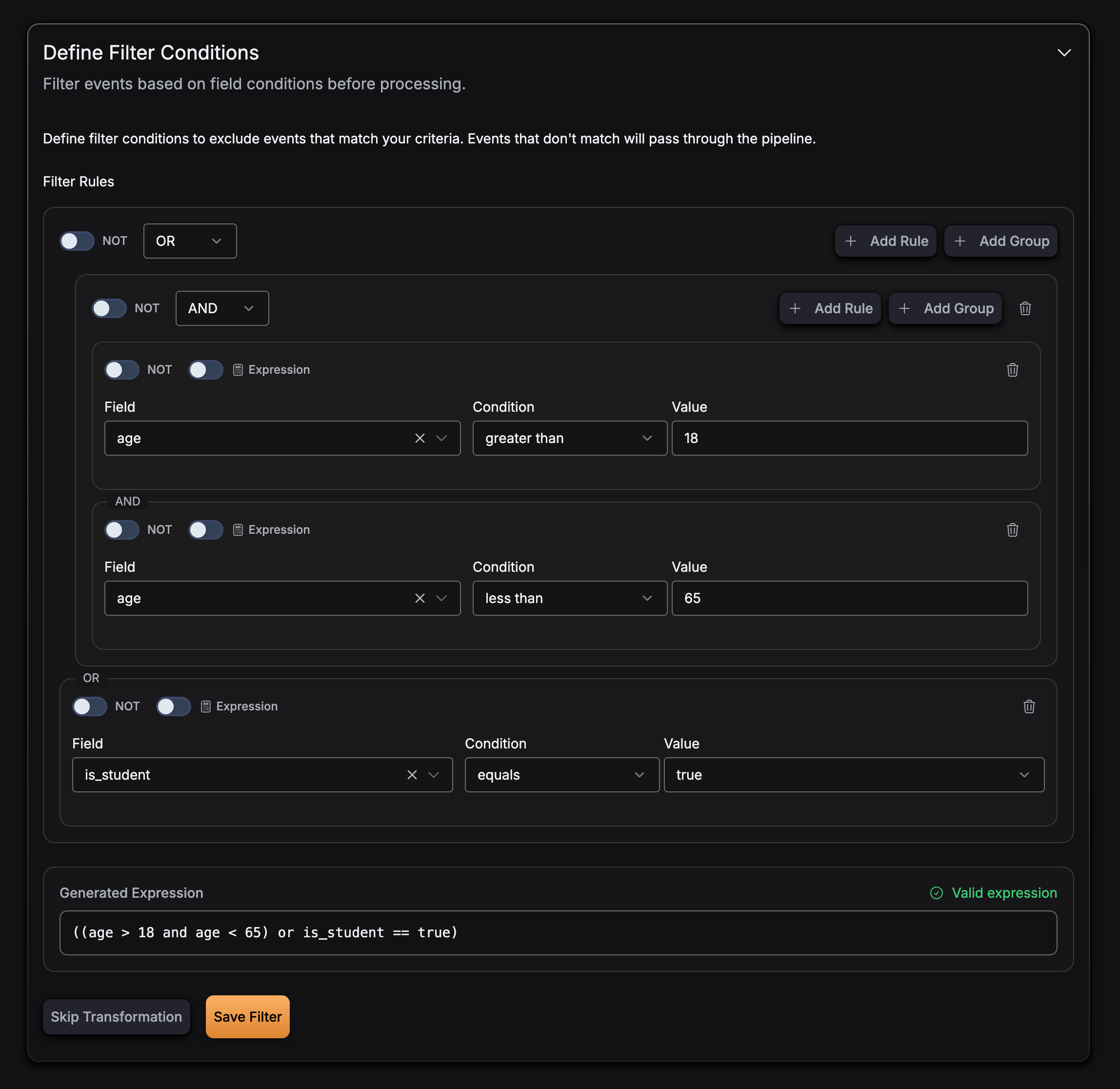
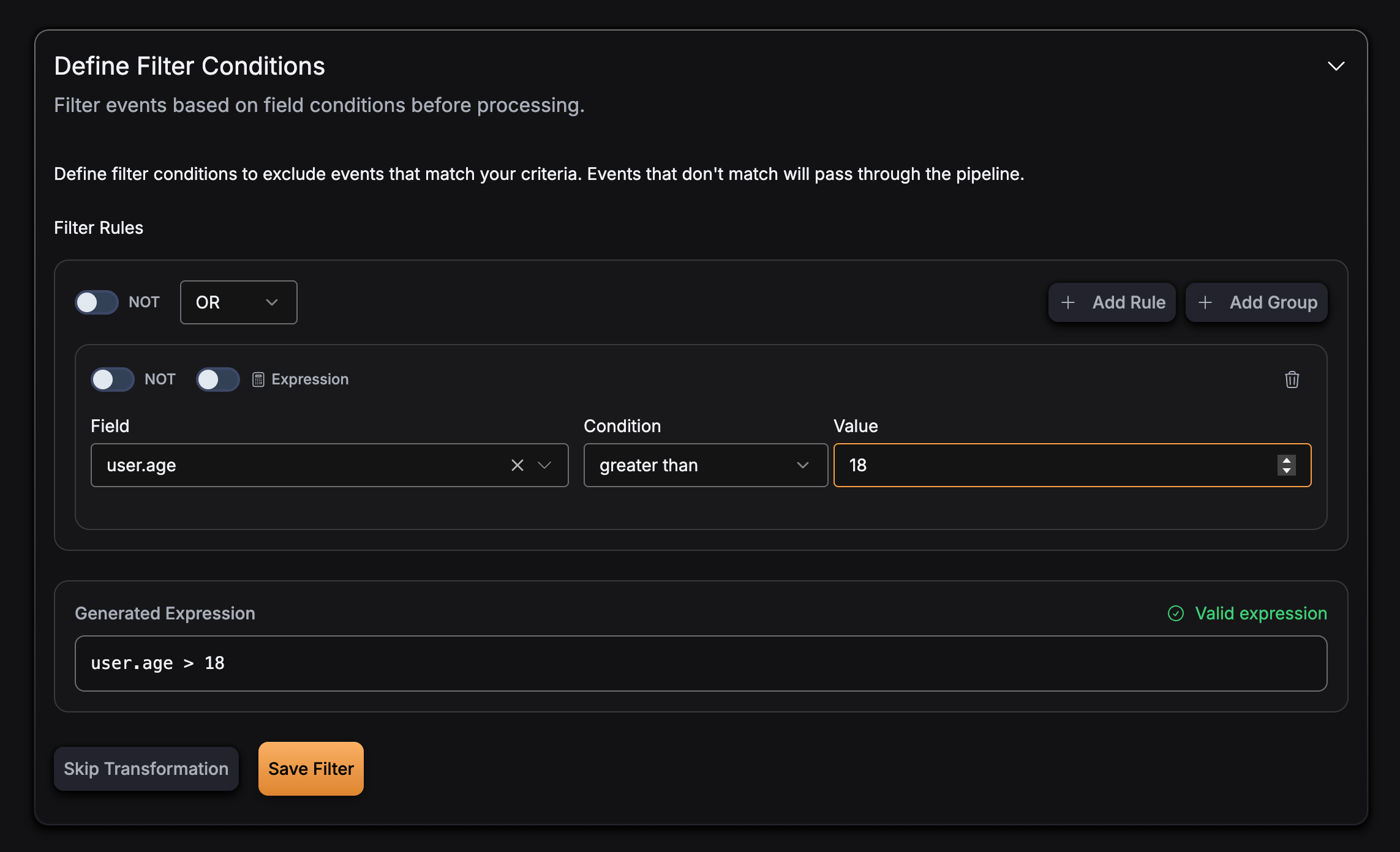
Expression Language
GlassFlow uses the expr expression language for filter expressions. This provides a simple, safe way to evaluate conditions on your event data.
Key Features:
- Field-based evaluation using event field names
- Support for common comparison operators (
==,!=,>,<,>=,<=) - Logical operators (
and,or,not) - Type-safe evaluation based on field types
Configuration
Filter is configured at the pipeline level. Here’s the configuration structure:
Expression Syntax
Filter expressions use field names from your event schema and support the following operations:
Comparison Operators
==- Equality!=- Inequality>- Greater than<- Less than>=- Greater than or equal<=- Less than or equal
Logical Operators
and- Logical ANDor- Logical ORnot- Logical NOT
Examples
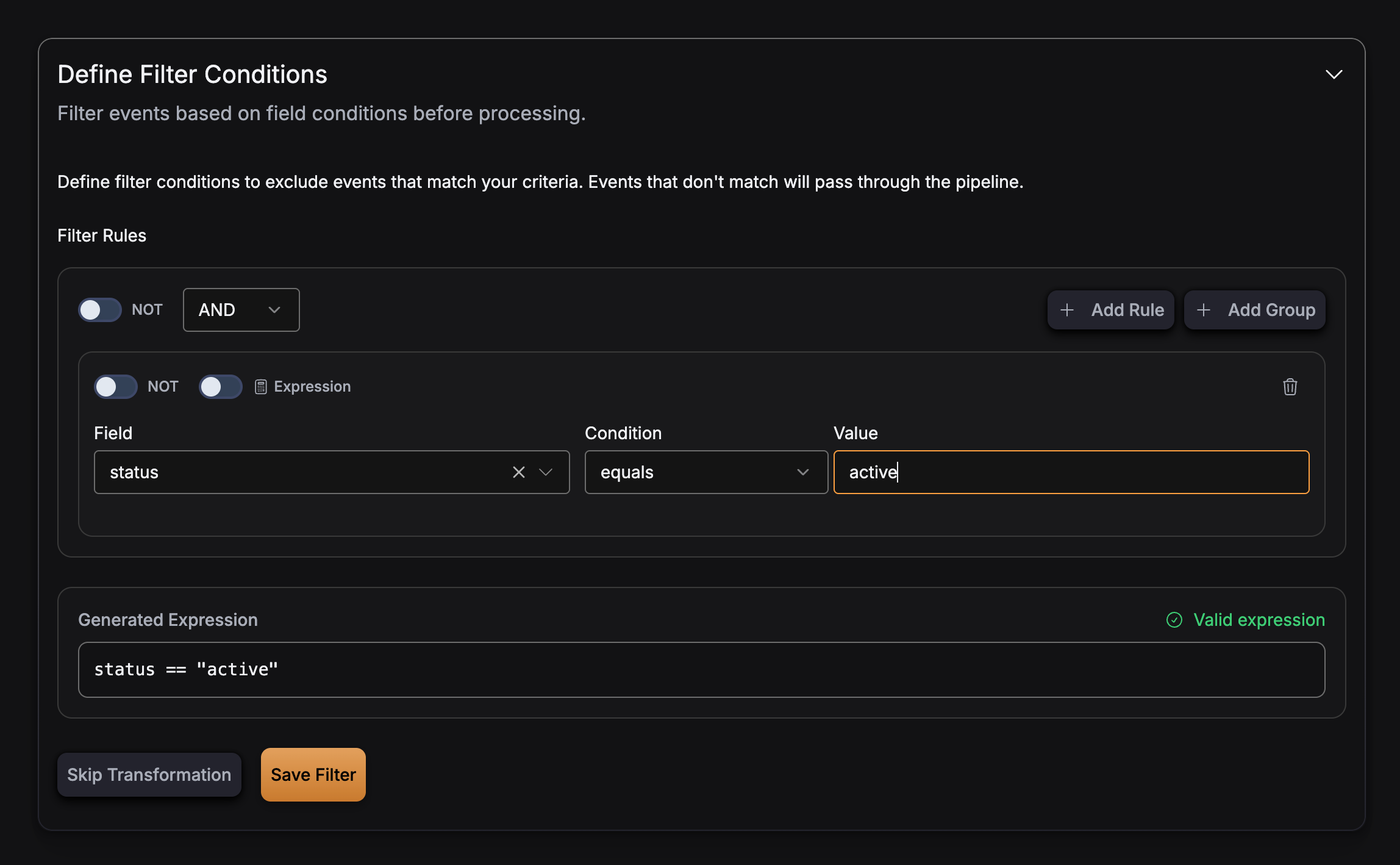
String comparison:
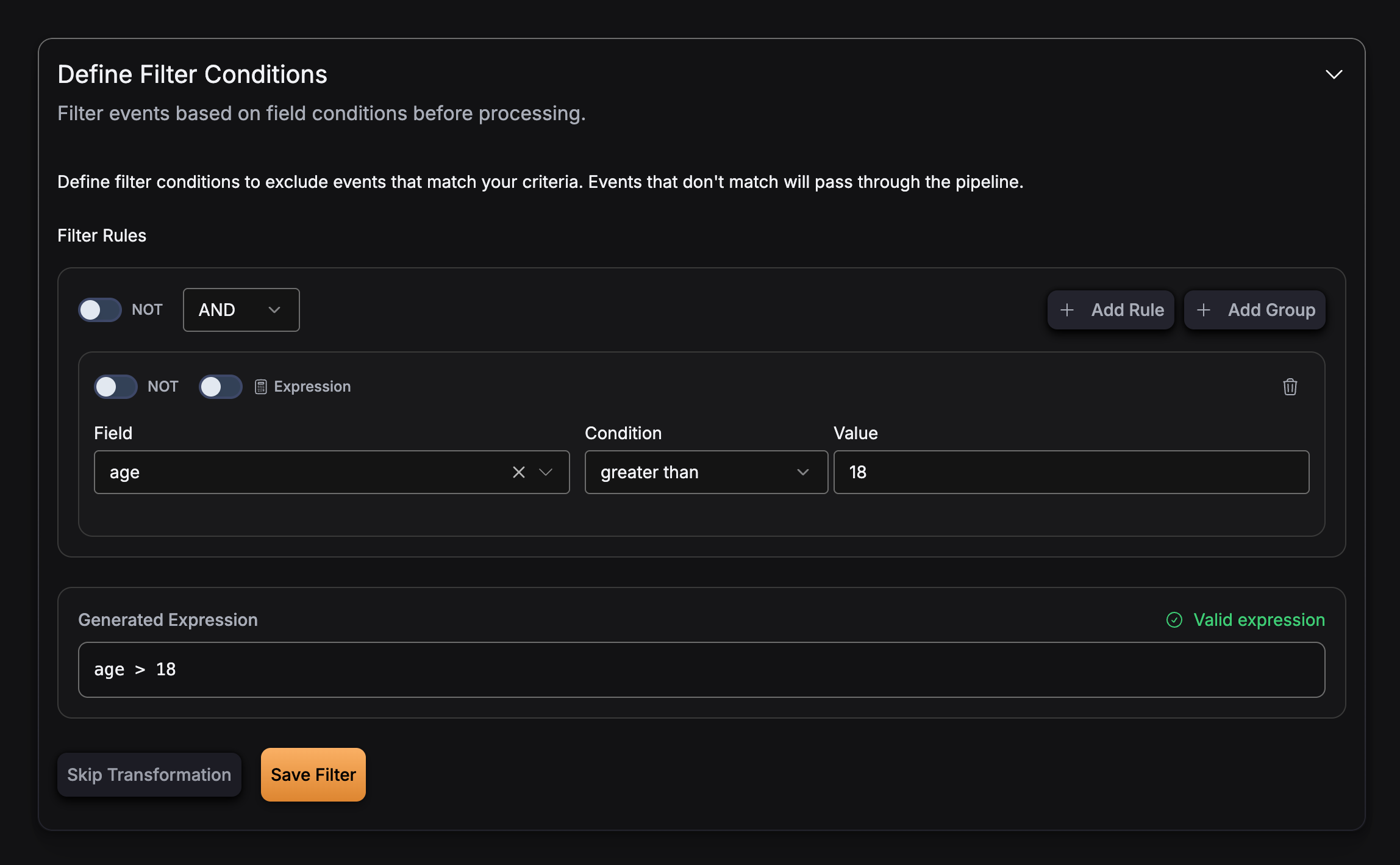
Numeric comparison:
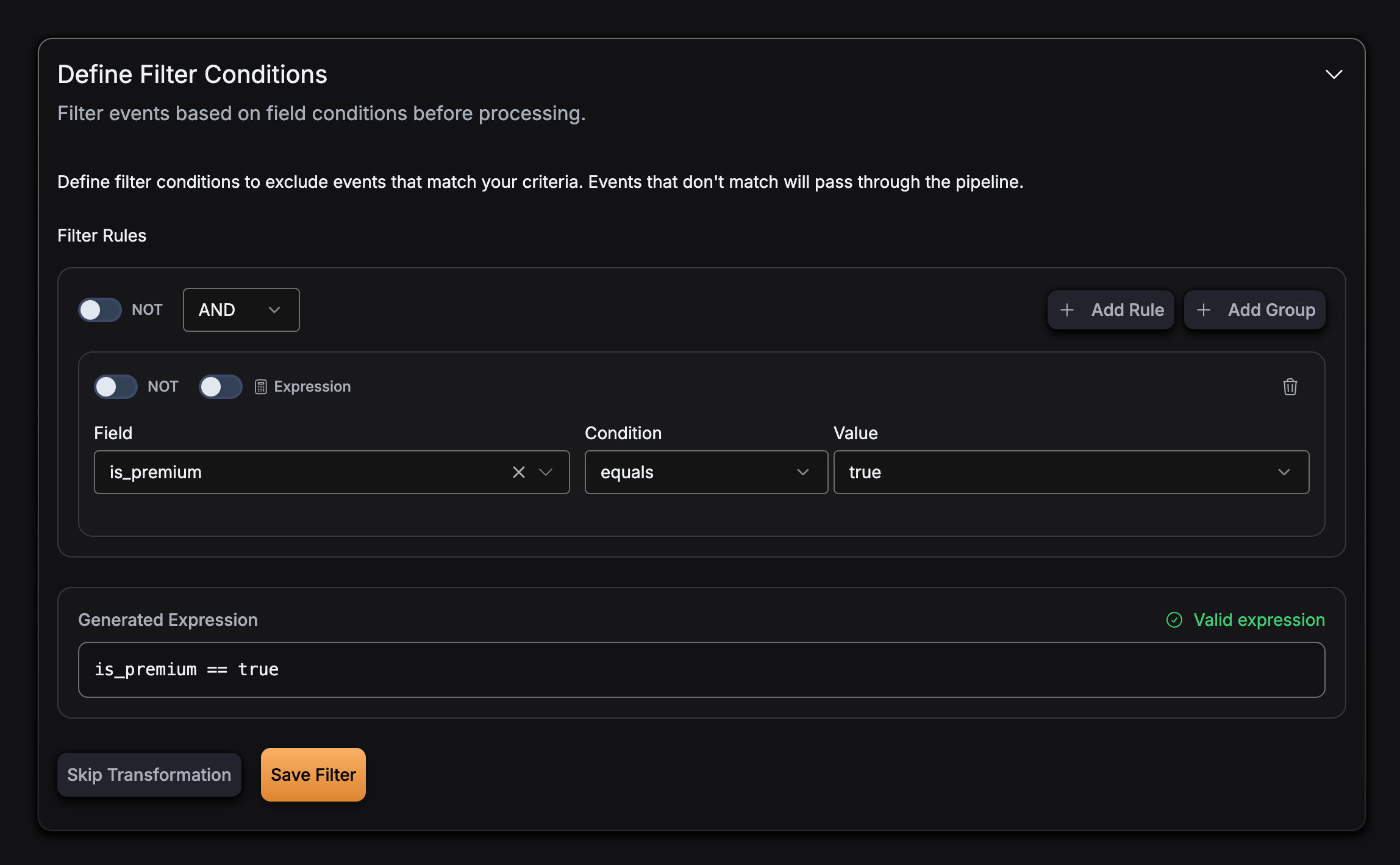
Boolean field:
Multiple conditions with AND:
Multiple conditions with OR:
Complex expression with parentheses:
Nested field access:
Best Practices
Expression Design
- Keep expressions simple: Complex expressions can be harder to maintain and debug
- Use parentheses: Explicitly group conditions with parentheses for clarity
- Test expressions: Validate filter expressions before deploying to production
Field Names
- Use exact field names: Field names in expressions must match exactly with your event schema
- Case sensitivity: Field names are case-sensitive
- Nested fields: Use dot notation for nested fields (e.g.,
user.age)
Type Safety
- Match field types: Ensure comparison values match the field types in your schema
- String literals: Use single quotes for string literals in expressions
- Numeric values: Use numeric literals without quotes for numeric comparisons
- Boolean values: Use
trueorfalse(lowercase) for boolean comparisons
Example Configuration
Here’s a complete example of a pipeline with filtering enabled:
{
"version": "v2",
"pipeline_id": "filtered-pipeline",
"name": "Filtered Events Pipeline",
"source": {
"type": "kafka",
"connection_params": {
...
},
"topics": [
{
"name": "user-events",
"consumer_group_initial_offset": "latest",
"replicas": 1
}
]
},
"filter": {
"enabled": true,
"expression": "age > 18 and status == 'active'"
},
"sink": {
"type": "clickhouse",
...
}
}