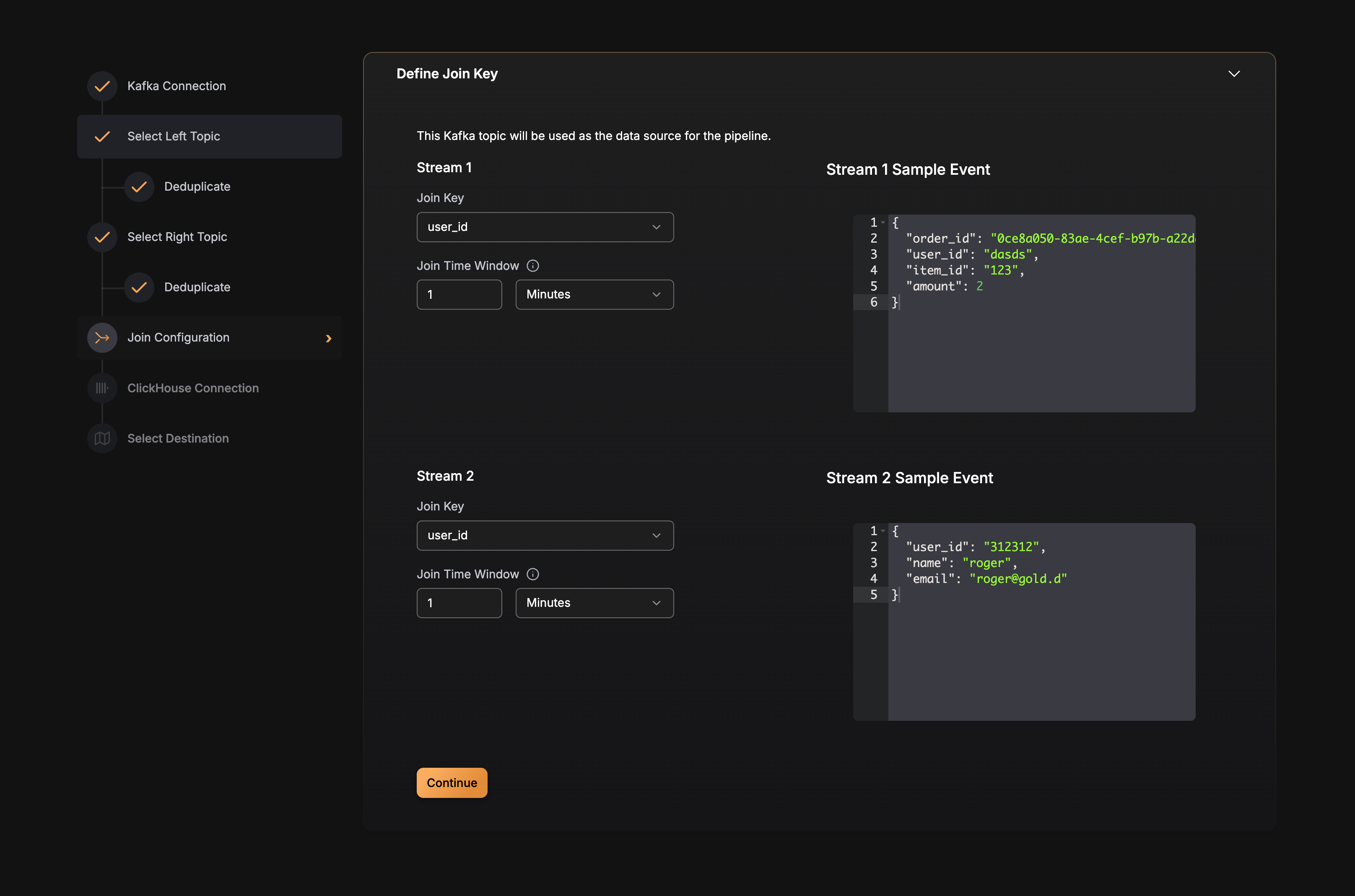
Join
The Join transformation combines data from multiple Kafka topics based on join keys and time windows. This enables you to enrich your data by merging related events from different sources using a temporal join algorithm.
How It Works
Join in GlassFlow uses a temporal join algorithm that matches events from different streams based on join keys within a configurable time window. The process maintains separate key-value stores for each stream to enable efficient matching.
Internal Process
The join service maintains separate key-value (KV) stores for the left and right streams:
Left Stream Processing
- When a message arrives from the left stream, the system looks up its join key in the right stream’s KV store
- If a matching key is found in the right KV store, the messages are joined and sent to the output stream
- If no match is found, the message is stored in the left KV store using its join key
- After a joined message is successfully sent to the output stream, the related left-stream message is removed from the left KV store
Right Stream Processing
- When a message arrives from the right stream, it is automatically stored in the right KV store
- The system then checks if a matching key exists in the left KV store
- If a match is found, the messages are joined and sent to the output stream
- The matched left-stream message is removed from the left KV store after successful join
Time Window and TTL
- Both left and right KV stores have a configured time-to-live (TTL) for each key, based on the join time window
- Entries are automatically evicted from the KV stores when their TTL expires
- This ensures that only messages within the configured time window are considered for joining
- Messages can be evicted only after they have been successfully joined and sent to the output stream, or when their TTL expires
Join Orientations
GlassFlow supports two join orientations:
- Left Join: All messages from the left stream are included, matched with right stream messages when available
- Right Join: All messages from the right stream are included, matched with left stream messages when available
For more details on the join algorithm, see the Data Flow documentation.
Configuration
Join is configured at the pipeline level. Here’s the configuration structure:
Best Practices
Choosing Join Keys
- Use stable identifiers: Join keys should be stable and consistent across both streams (e.g., order IDs, user IDs, product IDs)
- Avoid high-cardinality fields: Very high-cardinality join keys can increase memory usage
- Ensure key presence: The join key field must exist in both source topics
Setting Time Windows
- Match event arrival patterns: Set the time window based on the expected time difference between related events
- Consider processing delays: Account for potential delays in event processing or network latency
- Balance memory and coverage: Longer windows use more memory but catch matches over longer periods
- Avoid excessive windows: Very long windows may hold unmatched events unnecessarily
Join Orientation
- Left join: Use when you want all events from the first source, with optional enrichment from the second
- Right join: Use when you want all events from the second source, with optional enrichment from the first
- Choose based on data volume: Consider which stream has higher volume and should be the primary stream
Performance Considerations
- Memory usage: The KV stores size depends on the number of unique join keys within the time window
- Event ordering: Join works best when events arrive in roughly chronological order
- Unmatched events: Events that don’t find a match within the time window are evicted and won’t be joined
Example Configuration
Here’s a complete example of a pipeline with join enabled:
{
"version": "v2",
"pipeline_id": "joined-pipeline",
"name": "Orders and Payments Join Pipeline",
"source": {
"type": "kafka",
"connection_params": {
...
},
"topics": [
{
"name": "orders-topic",
"consumer_group_initial_offset": "latest",
"replicas": 1
},
{
"name": "payments-topic",
"consumer_group_initial_offset": "latest",
"replicas": 1
}
]
},
"join": {
"enabled": true,
"type": "temporal",
"sources": [
{
"source_id": "orders-topic",
"join_key": "order_id",
"time_window": "1h",
"orientation": "left"
},
{
"source_id": "payments-topic",
"join_key": "order_id",
"time_window": "1h",
"orientation": "right"
}
]
},
"sink": {
"type": "clickhouse",
...
}